Which Of The Following Would Not Shift The Demand Curve For A Good Or Service?
What is Elastic Need?
Elastic demand refers to an economic concept which states that the demand for a practiced or service changes with the fluctuations in its price. If a product has an elastic demand, it will take more buyers when its price goes downwardly and vice-versa.
The concept helps mensurate the extent to which a production or service'due south need is afflicted by external factors. It helps in deciding product pricing, inventory planning, marketing strategies and expected returns.
- Elastic demand states that a commodity'southward consumer demand spontaneously responds to its price change.
- The formula for the elasticity of demand = Percentage change in quantity/ Percentage modify in demand.
- When elasticity is higher than 1, it signifies products have an elastic demand. Such a need curve Demand Curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the prices of goods and demand quantity and is usually inversely proportionate. That means higher the cost, lower the need. It determines the constabulary of need i.e. equally the price increases, demand decreases keeping all other things equal. read more than is relatively flattened towards the x-axis, reflecting high sensitivity to alter.
- Luxury products, consumer durables and those commodities which have many substitutes experience high demand elasticity.
- Other than price, other determinants affect the need, such as consumer income, personal gustation, substitute bolt, etc.

You are gratuitous to use this paradigm on your website, templates etc, Please provide usa with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Rubberband Demand (wallstreetmojo.com)
Understanding Elastic Demand
Elastic demand reflects the change in a skilful or service'southward demand against a determinant. The upshot of price on need is studied under the price elasticity of need which relates to the police force of demand. The law states that other factors being constant, a decrease in a good'southward price will increase its demand and vice versa.
For example, luxury clothes have rubberband demand under the toll elasticity of demand. People unremarkably rush to luxury brands when they announce discounts to buy more. But when nosotros discover the reality, we realize that other factors such as consumer income, substitute goods, personal taste, etc., also affect the demand. A consumer could be addicted to a luxury brand of tea and buy it even after its cost skyrockets.
To mensurate the reaction of demand, elasticity comes into the picture show. The elasticity of demand measures the variability or extent to which the demand changes in response to a factor. The formula to measure if the demand is elastic or non is explained beneath.
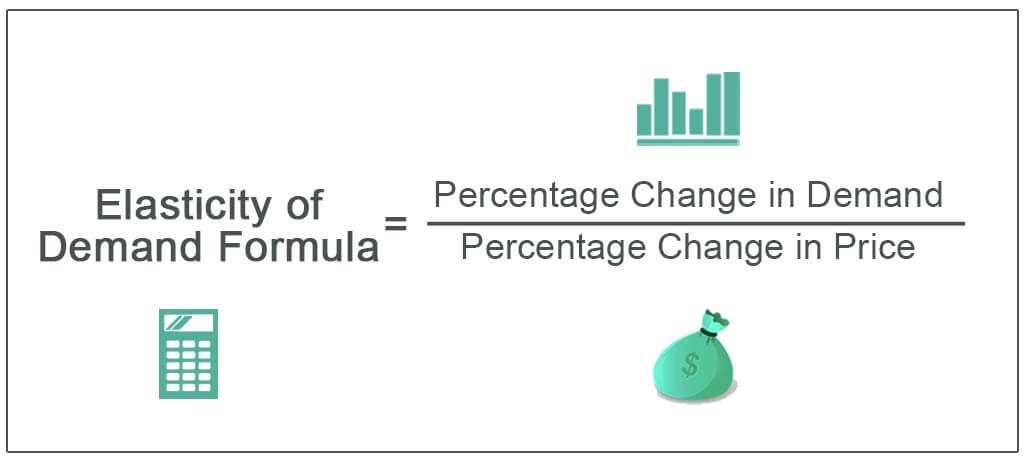
Elastic Demand Formula
Yous are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Elastic Demand (wallstreetmojo.com)
To find out if a product has rubberband demand, we will need to apply the elasticity of need formula. The formula for the elasticity of need is equally follows
Elasticity of Demand or Ed = Percentage alter in quantity/ Percent modify in cost
Percentage change in quantity = Change in Quantity/ Boilerplate Quantity
Change in quantity tin be constitute past deducting onetime quantity from new quantity.
Pct change in toll = Change in Toll/ Average Price
Modify in price can be found past deducting old price from new cost.
When we apply this formula, and the outcome is more than than one, it becomes the instance of rubberband demand. In other words, whenever the elasticity of need is more than ane, the demand will be sensitive to changes.
Elastic Need Curve
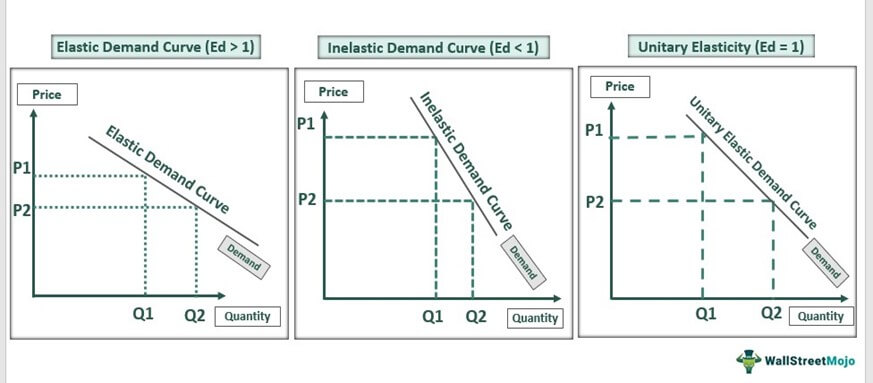
The elasticity of demand is above one when in that location is high responsiveness to change against a determinant such as price. This will also be seen in the graph. Under the price elasticity of demand, the elastic need graph will accept price on the y-centrality and quantity on the x-centrality. The demand curve will be relatively flattened towards the 10-axis, showing high sensitivity to price Price Sensitivity, also known and calculated by Price Elasticity of Need, is a measure of alter (in percentage term) in the demand of the product or service compared to the changes in the price. It is used widely in the business organisation earth to determine the pricing of a product or study consumer behavior. read more .
When the demand is not sensitive to price, information technology will result in inelastic demand. The demand for necessary goods such equally milk, electricity, fuel, medicines will not go down with an increase in price as people will buy them largely no matter what. They are an example of inelastic goods and have less than 1 elasticity.
Additionally, a product will accept unitary elasticity if its demand varies in verbal proportion to the pct change in its toll. Here, elasticity of demand is one.
Finally, under the definition of perfectly rubberband demand, the results volition change. The alter in a commodity'due south price will result in an space change in its demand. As such, if the price goes down, the demand will ascent to infinity and vice-versa. Hither the demand curve will be parallel to the x-axis.
Examples of Elastic Demand with Calculations
To better empathise this concept, permit'southward accept you lot through the following two examples:
Instance 1
ABC Electronics initially sold 1500 LED televisions a twelvemonth at $chiliad per TV. The price of LED Boob tube reduced to $900, and the need increased to 1800 units. Find the elasticity of need.
Percent change in demand =
(1800-1500) / (1500+1800/ii)
= 0.125
Percentage change in price = (900-1000) / (1000+900/2)
=0.x (ignore the – sign)
Elasticity of Demand or Ed =0.125/0.10
Ed=1.25
Hence, the company experienced elastic demand since Ed˃1, signifying the alter in demand is college than the change in the price of LED TVs.
Example 2
XYZ Beverages Ltd. produces java. The initial price of coffee was $80 per kg, and the quantity demanded Quantity demanded is the quantity of a particular article at a particular price. It changes with alter in price and does non rely on market place equilibrium. read more per month was 1200 kgs. The price rose to $100 per kg, simply the quantity demanded decreased to 1150kgs. Find the elasticity of demand.
Percentage modify in demand =
(1150-1200) / (1200+1150/ 2)
= 0.02
Percentage modify in price =
(100-fourscore) / (fourscore+100) /2)
= 0.11 (ignore the – sign)
Ed = 0.02/0.11
Ed = 0.18
Since, Ed˂1, the change in demand is non that significant to the alter in the toll of coffee.
Other Determinants of Elasticity
Except for or along with price, diverse other factors contribute to the change in demand for goods or services. The elasticity of demand is calculated for many of these factors also. These determinants are stated below:
- Consumer Income: A downfall in the consumers' income results in decreased need for a production or service. Say, John visited a buffet iv times a calendar month, just he restricted it to ii due to a decline in his income.
- Substitute Goods: The commodities with substitutes experience volatile demand since the consumer can ever switch to substitutes Any alternative, replacement, or fill-in of a primary product in the market is referred to as a substitute product. It refers to any commodity or combination of goods that might exist used in identify of a more pop item in normal circumstances without affecting the composition, advent, or utility. read more if the production'south price increases. For case, if butter'south price increases, many volition shift to margarine to not impact their upkeep.
- Complementary Goods A complementary adept is i whose usage is direct related to the usage of another linked or associated skilful or a paired good i.e. we tin say two goods are complementary to each other. read more than : If the toll of a good rising, it will also affect the need for its complementary. For example, if the toll of vegetables becomes high, vegetarian food price will likewise go upwards in the restaurants. Information technology volition affect the need of both.
- Necessity: Even when the price of necessary goods similar flour or rice goes up, their demands do not vary much. On the other hand, if luxury products or services such as imperial vacation packages rise in price, their demand falls.
- Time: Time is another essential factor; many times, a product's need doesn't fall in the short run A Brusque Run in economic science refers to a manufacturing planning period in which a business organisation tries to meet the market demand past keeping ane or more production inputs fixed while changing others. read more even after its price ascension similar iPhone's paid applications. However, the client can program to change the mobile phone in the long run to avoid the high costs of such apps.
- Customer gustatory modality and preference: If consumers prefer a product, say a particular brand of wear, they will keep buying information technology despite the price rising.
FAQs
What is elastic and inelastic?
A production whose demand among the consumers varies significantly with the variation in its cost is termed elastic. On the contrary, a commodity whose price change hardly impacts its demand is known as inelastic.
What happens when demand is elastic?
Since in elastic demand, the price changes slightly, just the quantity demanded varies drastically. The need curve here appears flatter and closer to the x-axis. As the need elasticity increases, this curve flattens fifty-fifty more.
What is elastic demand example?
One of the best examples of elastic need is the downfall in demand for gold jewellery when the gold price is loftier.
How do you know if need is elastic?
When nosotros utilise the formula for elasticity of demand which is – percentage change in quantity/ percentage change in demand, the result will help us understand if the demand is rubberband or not. If the elasticity or outcome is more than 1, the demand is sensitive to modify.
Is salt elastic or inelastic?
Salt is inelastic because fifty-fifty if its cost goes high, its demand will non be much affected since it is an essential product.
Recommended Manufactures
This has been a guide to What is Rubberband demand and its Definition. Here we hash out the formula of Elastic Demand along with its curves and applied examples. You can larn more about economics from the following articles –
- Pinnacle Inelastic Demand Examples
- Examples of Elasticity of Demand
- Formula of Cross Toll Elasticity of Need
- Giffen Goods
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/elastic-demand/
Posted by: basssignitere.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Would Not Shift The Demand Curve For A Good Or Service?"
Post a Comment